admin
Neurologic Complications of Peripheral Nerve Blocks
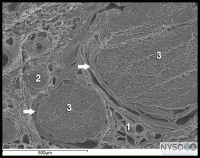
Author: Jeff Gadsden Nerve injury following peripheral nerve blockade (PNB) is a potentially devastating complication that can result in permanent disability. (1) Data ...
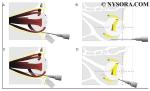
Ultrasound-Guided Wrist Block
A B C Figure 1: Ultrasound-guided wrist block. Transducer and needle positions for (A) Median nerve block, (B) Ulnar nerve block, (C) Radial nerve block. Essentials ...
Ultrasound-Guided Forearm Block
A B C Figure 1: (A) Radial nerve block above the elbow. The needle is inserted in-plane from lateral to medial direction. (B) Median nerve block at the ... Full story
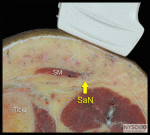
Ultrasound-Guided Saphenous Nerve Block
Figure 1: Needle insertion to block the saphenous nerve at the level of the mid thigh (left) or below the knee (right). Essentials Indications: saphenous vein ... Full story
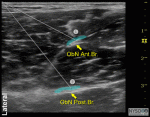
Ultrasound-Guided Obturator Nerve Block
Figure 1: Needle insertion using an in-plane technique to accomplish an obturator nerve block. Essentials Indications: Relief of painful adductor muscle contractions, top revent adduction of ... Full story
Ultrasound-Guided Fascia Iliaca Block
Figure 1: Needle insertion for the fascia iliaca block. The black dot indicates the position of the femoral artery. Essentials Indications: anterior thigh and knee surgery, ... Full story
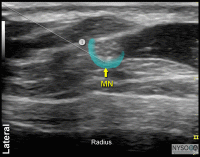
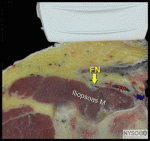
Ultrasound-Guided Femoral Nerve Block
Figure 1: Transducer position and needle insertion using an in-plane technique to block the femoral nerve at the femoral crease. Essentials Indications: anterior thigh, femur, and ... Full story
Continuous Peripheral Nerve Blocks in Outpatients
Introduction - Single-injection nerve blocks provide up to 16 hours of postoperative analgesia - Portable infusion pumps allow outpatients to receive continuous nerve blocks More than 40% of ... Full story
Indications for Peripheral Nerve Blocks
AUTHOR: Jeff Gadsden Introduction During the past 20 years, increasing knowledge in functional regional anesthesia anatomy, coupled with new technologies for locating peripheral nerves, has resulted in ... Full story
Thoraco Lumbar Paravertebral Block
Overview Indications: Inguinal hernia surgery, lateral abdominal wall surgery Landmarks: Spinal processes T9-L5 (the number and location of levels chosen for each indication) Transverse process Needle insertion: 2 cm lateral ... Full story
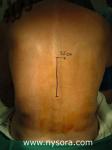
Continuous Thoracic Paravertebral Block
Overview Indications: Breast surgery, pain management after thoracic surgery or rib fractures Landmarks: Spinal process at the desired thoracic dermatomal levels Needle insertion: 2.5 cm lateral to midline Target goal: ... Full story
Caudal Anesthesia
Caudal anesthesia was first described at the turn of last century by two French physicians, Fernand Cathelin and Jean-Anthanase Sicard. The technique predated the lumbar ... Full story
Local & Regional Anesthesia for Eye Surgery
--- Authors: Jacques Ripart, MD; Kenneth Mehrige, MD; Robert Della Rocca, MD Introduction Ophthalmic surgery is one of the most frequent surgical procedures requiring anesthesia in developed ... Full story
Obturator Nerve Block
Obturator nerve block is used to treat hip joint pain and in the relief of adductor muscle spasm associated with hemi-or paraplegia. Muscle spasticity is relatively common problem among patients suffering from central neurological problems such as cerebrovascular pathology, medullar injuries, multiple sclerosis, infantile cerebral palsy, etc. ... Full story
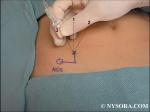
Ilioinguinal and Iliohypogastric Blocks
Introduction "Almost all cases of hernia, with the possible exception of those in young children, could undoubtedly be subjected to the radical operation under local anesthesia." ... Full story
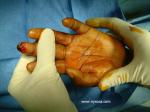
Digital Nerve Block
A digital block is the technique of blocking the nerves of the digits to achieve anesthesia of the finger(s). This technique is simple to perform ... Full story
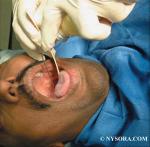
Regional & Topical Anesthesia for Endotracheal Intubation
Introduction Recent developments in regional anesthesia have resulted in a number of innovative and refined options to practitioners, often allowing regional techniques to be used for ... Full story
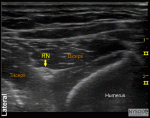
Ultrasound-Guided Axillary Brachial Plexus Block
Figure 1: Transducer position and needle insertion in ultrasound-guided axillary brachial plexus block. Essentials Indications: forearm and hand surgery Transducer position: short axis to arm, just distal to ... Full story
Ultrasound-Guided Infraclavicular Brachial Plexus Block
Figure 1: In-plane needle insertion technique during infraclavicular brachial plexus block. Essentials Indications: arm, elbow, forearm, and hand surgery Transducer position: approximately parasagittal, just medial to coracoid process, ... Full story
Ultrasound-Guided Interscalene Brachial Plexus Block
Figure 1: Ultrasound-guided interscalene brachial plexus block; transducer and needle position to obtain the desired ultrasound image for an in-plane approach. Essentials Indications: shoulder and upper ... Full story
Ultrasound-Guided Superficial Cervical Plexus Block
Figure 1: Needle and transducer position to block the superficial cervical plexus using a transverse view. Essentials Indications: carotid endarterectomy, superficial neck surgery Transducer position: transverse over ... Full story
Equipment for Peripheral Nerve Blocks
Ali Nima Shariat, Patrick M. Horan, Kimberly Gratenstein, Colleen McCally, and Ashton P. Frulla Introduction Over the past several decades, regional anesthesia equipment has undergone ... Full story
Author info
adminLatest comments